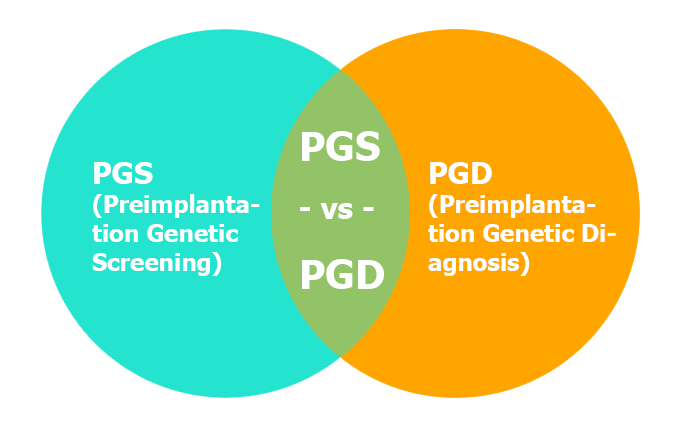
Preimplantation Genetic Screening (PGS)
What is PGS ?
Pre-implantation Genetic Screening (PGS) is a technique used to detect chromosomal abnormality of IVF embryo. PGS takes a biopsy cell(s) sample from embryos (refer to Picture 1) and evaluates or test for chromosomal abnormality. Embryos that test chromosomally normal (euploid) are then considered for embryo transfer into uterus.
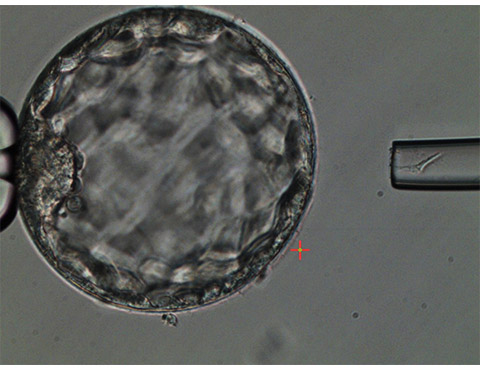
Picture 1
PGS is recommended to cases as follows:
- Advanced maternal age. The incidence of chromosomal abnormality (aneuploidy rate) has been validated to increase with women age
- Recurrent miscarriage
- Repeated implantation failure
- Severe male infertility
- Previous Chromosomally abnormal pregnancy
PGS & Benefits
Having a healthy baby is the expectation of each parent. PGS decreases risk to couples or individuals with serious inherited disorders of having children affected with same problem. PGS does increase the efficiency of IVF by improving embryo selection, thereby increasing the IVF outcomes as follows:
- Increase in likelihood having healthy baby
- Increase pregnancy rate per transfer
- Reduction in miscarriage
- Reduction in time and necessary resources to achieve pregnancy
- Reduces risk of multiple pregnancy

Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD)
What is PGD ?
Pre-implantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD) takes a biopsy cell(s) sample from embryos to diagnose embryos for known genetic disorder that both patient and partner are carriers prior to transfer to uterus. PGD can prevent transmission of these this disorder ie, monogenic diseases due to the function of gene is altered by change in the specific sequence, called mutations. These mutations can be transmitted in families from generation to generation.
PGD is recommended to couples with personal of high risk in the families for any of the following monogenic diseases:
- BetaThallasemia
- Cystic fibrosis
- Hemophilia A (F8)
- Hemophilia B (F9)
- Fragile X Syndrome
- Spinal muscular atrophy
- X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy
- Huntington’s disease
- Autosomal Dominant/ Recessive Polycystic kidney disease & etc